Describe Azure role-based access control
The principle of least privilege should be used. So that only the needed privileges are acquired by a user.
Doing this individually for each user is not feasible. So Azure role-based access control (also called Azure RBAC) is able to do that with roles.
Own roles can be created.
How is it applied to resources?
RBAC is set to a scope, view the diagram from Microsoft below:
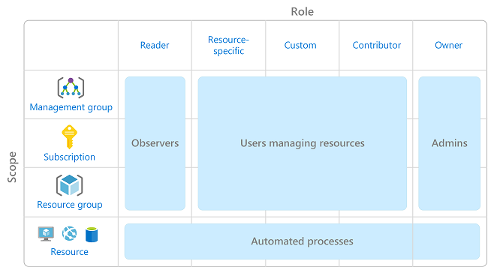
Scopes include:
- Management group (collection of multiple subscriptions)
- Single subscription
- Resource group
- Single resource
BE AWARE: The permissions you set on the parent of a Role, will also be inherited by its children.
How can it be enforced?
- It is always enforced on any action which goes through Azure Resource Manager.
- Resource Manager can be accessed through Az Protal, CLI and so on
- Application and data level access security is NOT controlled by RBAC
- RBAC uses allow model
- Meaning, when I got a role with read access to a resource and another group I got write access to the same resource, I got both read and write in the end.