Defense-in-Depth
Protect information and prevent them from being stolen from people who shouldn't be able to access it.
Layers
Graph from MS:
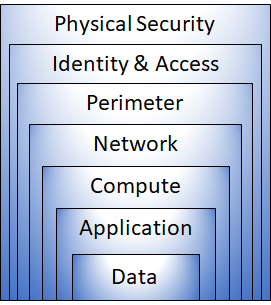
If one layers is breached, the next one will try to protect it again.
Physical security
This is securing a building for example with security personnel, cameras or fences.
Identity and Access
It ensures that the identity of a user is secure, verified and is eligible to access the resources.
It is important to:
- Use control access to infrastructure and change control
- Use SSO and MFA
- Check events and changes (log and evaluate/audit)
(Network) Perimeter
It protects from network-based attacks against services. It is important to identify and protect the network boundaries.
It is important to:
- Use DDoS protection
- Use firewalls
Network
Limiting the access for the services inside the network. So only the services which need to communicate with each other can do that. With that the risk of a spreading attack is dimmed.
It is important to:
- Limit communication between services
- Deny by default
- Restriction of inbound and outbound access
- Secure connectivity to on-premises networks
Compute
Malware can be installed on a machine. So it is important to secure the machines. Also not installing patches can be a problem.
It is important to:
- Access control to VMs
- Endpoint protection and keep system patched
Application
Application should be secure by standard. Integrating security in the application lifecycle can avoid bugs.
It is important to:
- Applications hsould be secure by standard and have no vulnerabilites
- store sensitive secres in a secure medium
- Make security a design requirement
Data
I as the person who stores and control access to the data is responsible to keep it secure. Mostly there are regulations by the government on how to store data (How long and till when)
Attackers are usually after the data of the following:
- DB
- VM disks
- SaaS apps (MS 365)
- Cloud storage